Body fat is essential to keeping our bodies healthy, because not all body fat is bad. The cardiovascular and central nervous system needs it, as well as our skeletal, endocrine, and reproductive systems. It is an energy source, and after about half an hour of exercise, when the carbohydrate reserves are depleted, your body starts to draw energy from fat.
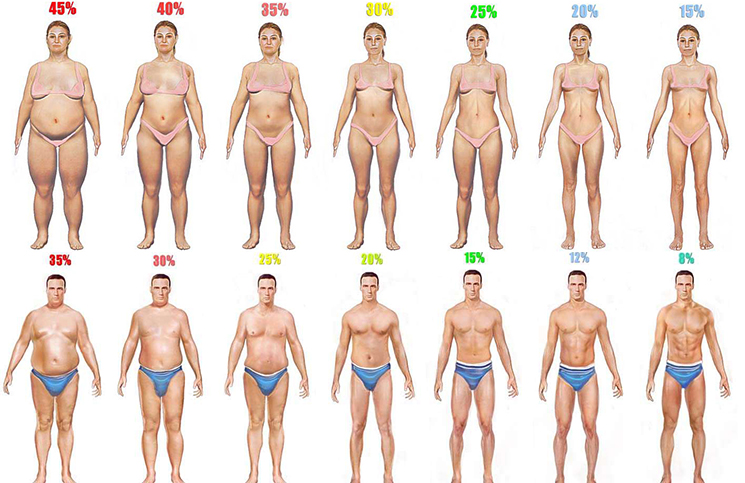
Leaner doesn’t always mean better. About 15-20 percent of body fat is required, so our bodies could function properly, and having fat percentage beneath that number has its negative effects. Male bodybuilders go below 5 percent, which is an alarming amount, but only when contesting (not staying below 5 percent all the time). Read and see what happens when body fat percentage goes lower than it should.
Muscle Strength & Recovery
After a workout session, or other activities which include heavy physical actions, your muscles need recovery, glycogen, and stored carbs. With low amounts of body fat, rehabilitation gets slowed down. When exercising, muscles get broken down (a process named catabolism), but they actually grow during the process of recovery, not in the gym. If we add lowering of testosterone level to this, you likely won’t be pumping your muscles any bigger.
Bone Strength
Calcium and vitamin D, without enough body fat, can’t be absorbed well. It leads to low bone density and, in some cases, osteoporosis.
Cardiovascular System
Low body fat can affect the cardiovascular system and hinder normal functioning of the heart. For example, by lowering their body fat, bodybuilders’ heart rate falls down to 27 bpm (beats per minute). Bradycardia (too low heart rate) can lead to passing out and chronic fatigue. An imbalance of electrolytes and improper caloric intake, due to low body fat percentage, can also be a cause of sudden cardiac arrest and arrhythmia.
Energy Levels
There is a decrease in energy levels due to having body fat percentage beneath the required 20 percent. Body fat is an energy reserve, and when you burn the energy that comes from carbohydrates and proteins, your body doesn’t have where to take more from. It limits your everyday functioning, and especially your workouts, making you unable to perform at optimal levels. Body fat also insulates our organs and maintains our body’s temperature. Not enough body fat causes the constant feeling of being cold. It can affect the thyroid gland, which controls many processes in our bodies, like the body’s internal thermostat, among others.
Skin
Dehydration is what brings us to having unhealthy skin. Having fats in your diet and eating lots of water-storing carbs would prevent skin dryness, wrinkles, and splotchy look. Some people even go vegan in order to get rid of the subcutaneous fat tissue, among other things. Amino acids, especially Omega-3 fatty acids (found in fish such as salmon, sardines, tuna, and lake trout), support skin cell turnover and reduces inflammation. You can read here about why their justifying reasons for dismissing fat are misleading.
Testosterone Levels
Leptin (also known as “fat hormone” and “obesity hormone”) is a hormone made in the fat cells which regulates energy balance. Testosterone is just one of the factors that affect leptin levels. Low leptin level tells the testicles, through a chain of reactions and signals, to produce less testosterone, which leads to fatigue, lack of energy, loss of muscle mass, low sex drive, and mood changes.
Immune System
The immune system is a complex set of biological processes and structures that contains a protective function against external body invaders. Low-fat diets can have negative effects on your immune system, making you susceptible to various infections, diseases, and inflammation. Many different kinds of cells, including fat cells, make the immune system, and their balance must be achieved so your body will be protected. Low body fat leads to the increase of cortisol levels, which impedes the immune system.
Mood
Nutrient intake affects the production of neurotransmitters, both directly and indirectly. The brain needs fats, which are the fuel for neurologic functions. Thus, low levels of body fat can cause frequent mood swings, irritability, or even depression. Having extremely low body fat level leads to lowering serotonin in the brain, causing depression in people who are more susceptible to it.
Having low body fat affects your immune system, making you prone to health problems, and decreases your physical performance. Body fat is needed for every body function – skeletal, cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, endocrine and central nervous system. If you’re not an elite athlete, and you don’t plan to become one, then there is no reason for you to fear fat. It has more functions than you thought it did, and going extreme in losing fat has a lot of setbacks.
By Mathews McGarry | [email protected]
One Response